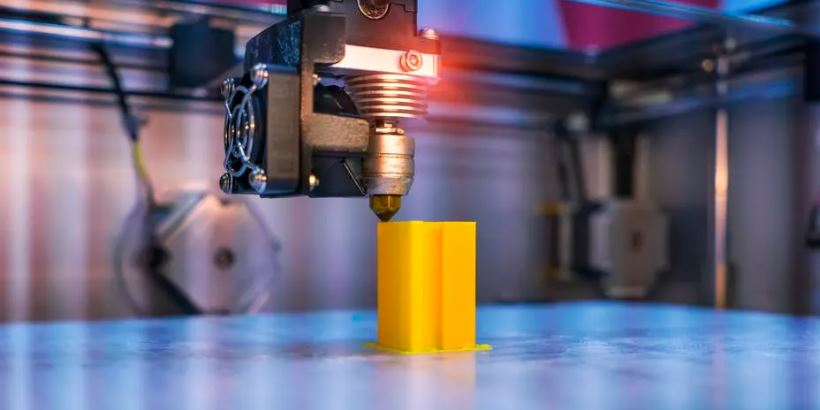
3D printing is a process in which a digital model is turned into a tangible, solid, three-dimensional object, usually by laying down many successive, thin layers of a material. 3D printing has become popular so quickly because it makes manufacturing accessible to more people than ever before. This is partly due to the price (the starting price for a basic 3D printer is about $300), but also the small size of the printers compared to traditional manufacturing.
Watch the video below to learn about the process of 3D printing.
How does it work?
First, a virtual design of the object is made. This design will work like a blueprint for the 3D printer to read. The virtual design is made using computer-aided design (CAD) software, a type of software that can create precise drawings and technical illustrations. A virtual design can also be made using a 3D scanner, which creates a copy of an existing object by basically taking pictures of it from different angles.
Once the virtual model is made, it must be prepared for printing. This is done by breaking down the model into many layers using a process called slicing. Slicing takes the model and slices it into hundreds or even thousands of thin, horizontal layers using special software.
After the model has been sliced, the slices are ready to be uploaded to the 3D printer. This is done using a USB cable or Wi-Fi connection to move the sliced model from the computer it’s on to the 3D printer. When the file is uploaded to the 3D printer, it reads every slice of the model and prints it layer by layer.
How are things printed?
The 3D printer will begin printing the layers of material in a process known as material extrusion. Depending on the type of 3D printer and material being used, there are several methods of material extrusion.
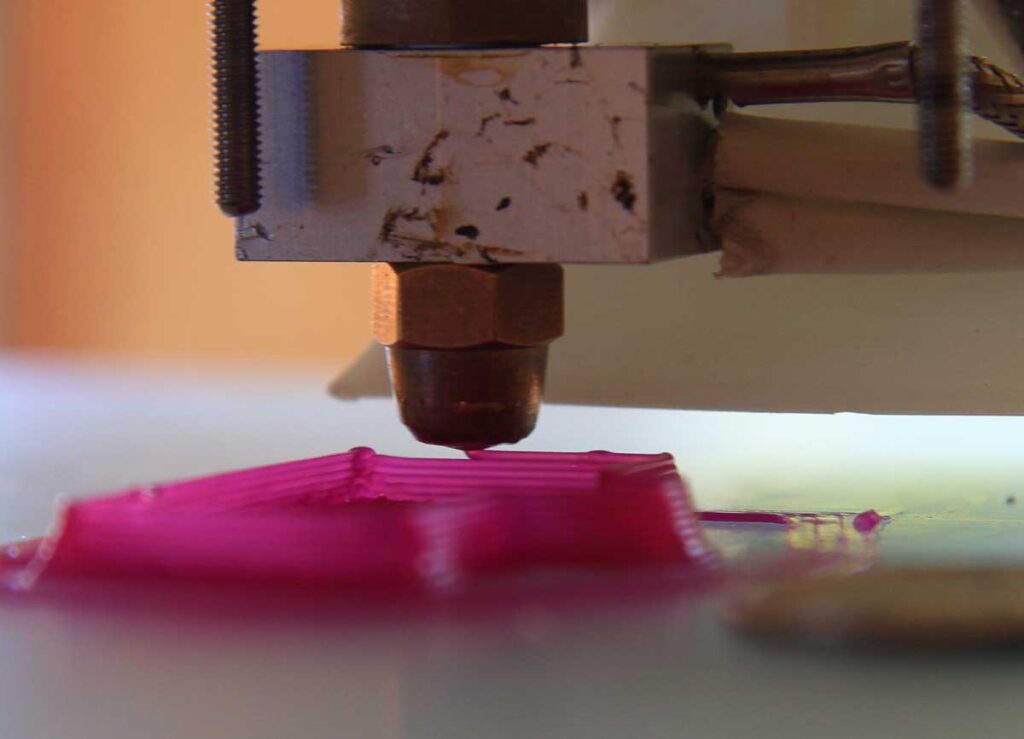
Most commonly, the 3D printer will have a nozzle ejecting a semi-liquid material, like molten plastic, metal, or cement. The extrusion nozzle can move in both horizontal and vertical directions as it precisely places the material, following the blueprint of the digital model layer by layer.
This process is repeated until the 3D printer has replicated every layer in the digital model with the extruded material.
Watch the time-lapse video below to see a 3D printer in action.
What sorts of things can be made with 3D printers?
Nearly anything you can imagine can be turned into a design that can be 3D printed. 3D printers are helping designers, engineers, and even everyday people create complex objects in ways previous manufacturing methods weren’t capable of.
3D printers are being used to create toys, phone cases, tools, clothing, tables, lamps, pottery, art, and even cars.

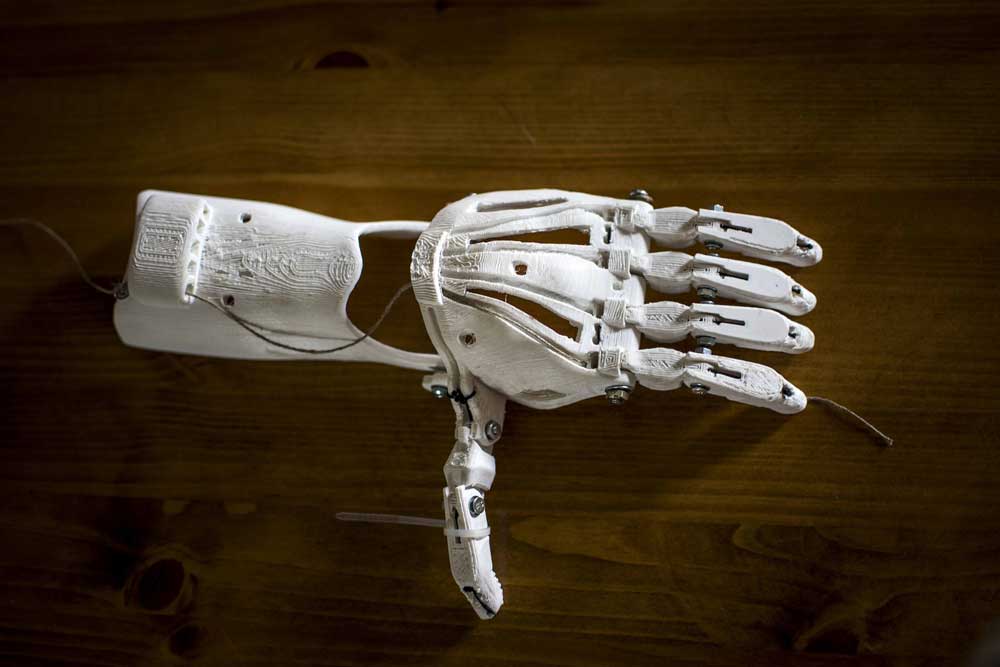
The medical field is also finding new ways to use 3D printing to help patients. Doctors are now able to print 3D medical models that are so accurate that surgeons can essentially do a practice run on a patient’s 3D model before actually operating on that patient. 3D printed models are also being used to create less expensive, more durable, and better-fitting prosthetics for individuals who have lost limbs.

3D printed production is a quickly evolving industry with a lot of exciting potential for the future. We’ve only just begun to see the ways 3D printed objects can make our lives easier, more convenient, safer, and healthier. And with 3D printing evolving as quickly as people can come up with new designs to print, it may not be long before we live in a world where you can 3D print your lunch, a custom fitted shirt, or replacement parts to repair everyday objects—all from the comfort of your own home.
Source:
https://edu.gcfglobal.org/en/thenow/what-are-genetically-modified-organisms-gmos/1/




